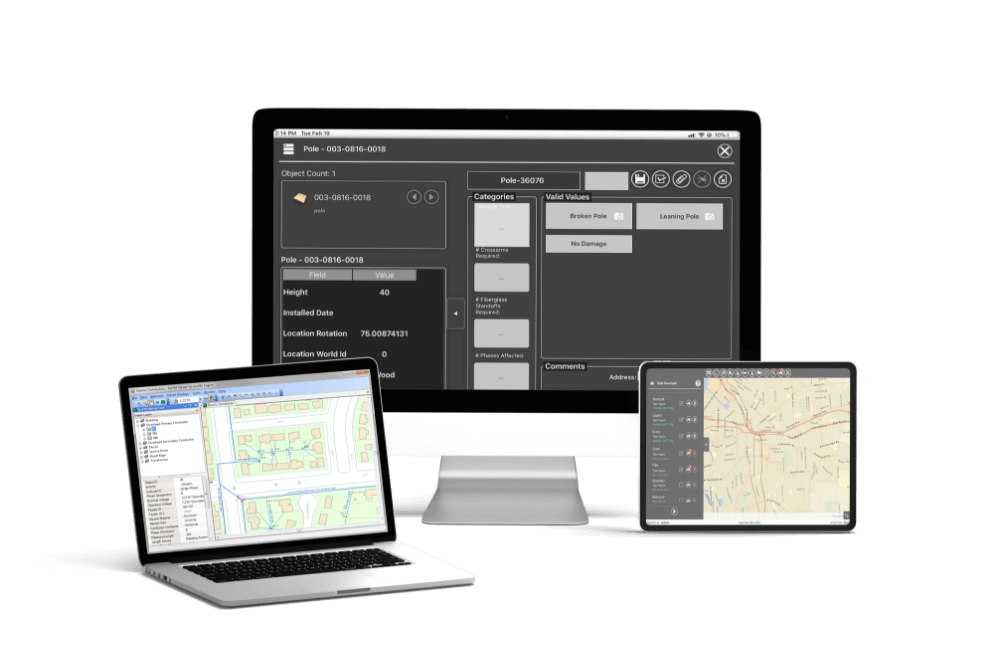
A Complete Guide to Field Service Management Using GIS for Utilities
The utility industry is going through digital transformation and companies in this space, whether electric or gas, are facing significant changes in many areas of their business. Perhaps the most critical is the need to adapt how field work is being managed and operationalized.